What’s “neural” about neural networks?
On the similarities and differences between artificial and natural intelligence
November 4, 2025
Agenda
- The (historical) relationship between neuroscience and AI
- Why AI researchers should care about neuroscience
- How to compare ANNs and brains
- Fundamental difference between ANNs and intelligent biological agents
How it started …

Neural computation: neurons can implement logical operations and networks of such neurons are capable of universal computation (McCulloch and Pitts 1943).

Hebbian learning: Randomly wired networks can learn through input driven reinforcement of synaptic connections (Hebb 1949)
How it’s going…

You can’t brute force intelligence
What is Intelligence ?
- Skill is how is the ability to perform a given task (e.g. playing chess)
- Intelligence is the ability to acquire-new skills and generalize to new problems (Chollet 2019)
- The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) is a set of tests aiming to benchmark intelligence (ARC leaderboard)
Example of an ARC task

Comparing Brains and Neural Networks
Relating Model Activation to Brain Recordings
- Show the same stimuli (e.g images) to Humans and Models
- Find mapping \(W\) between brain activity \(Y\) and model activation \(X\)
- Correlate the prediction from model activation to the actual brain recording: \(R^{(d)} = \text{corr}(WX_{test}, y_{test})\)

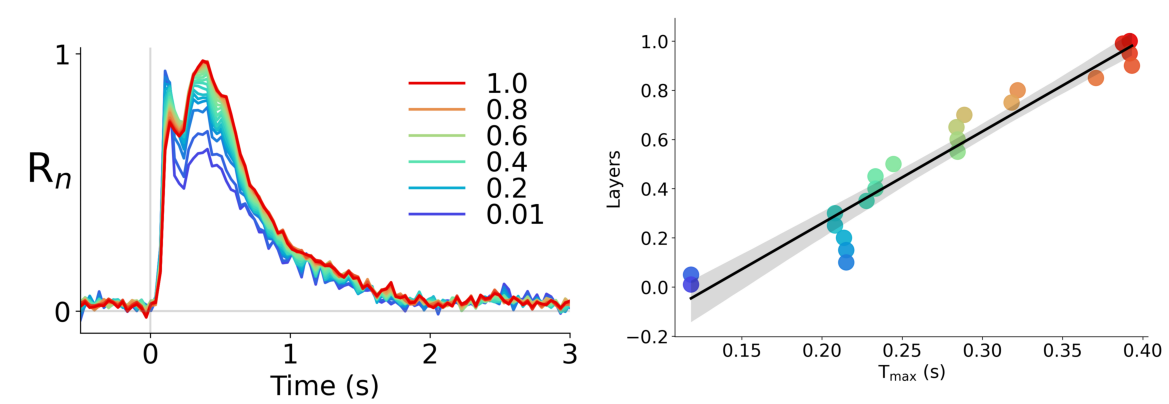
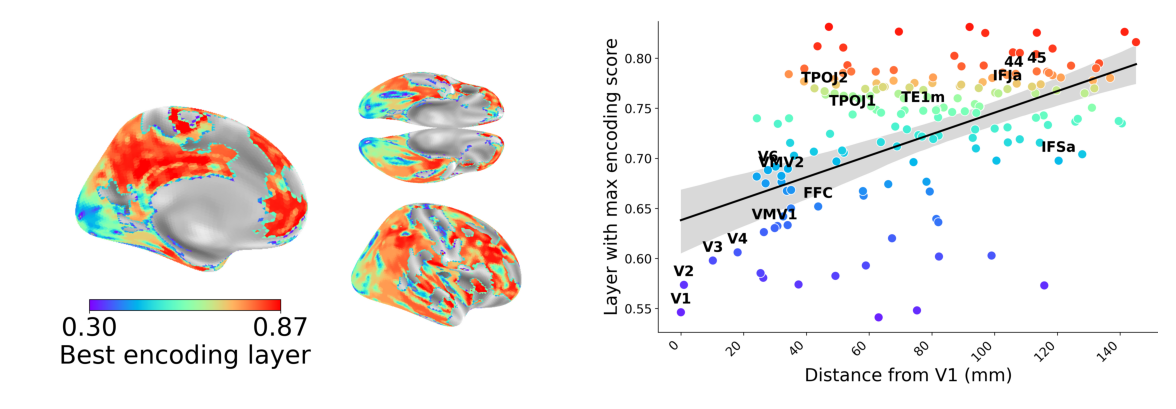
Corresponding Representational Hierarchies
Different Architecture, Convergent Solutions
- Better ImageNets are more predictive of brain activity
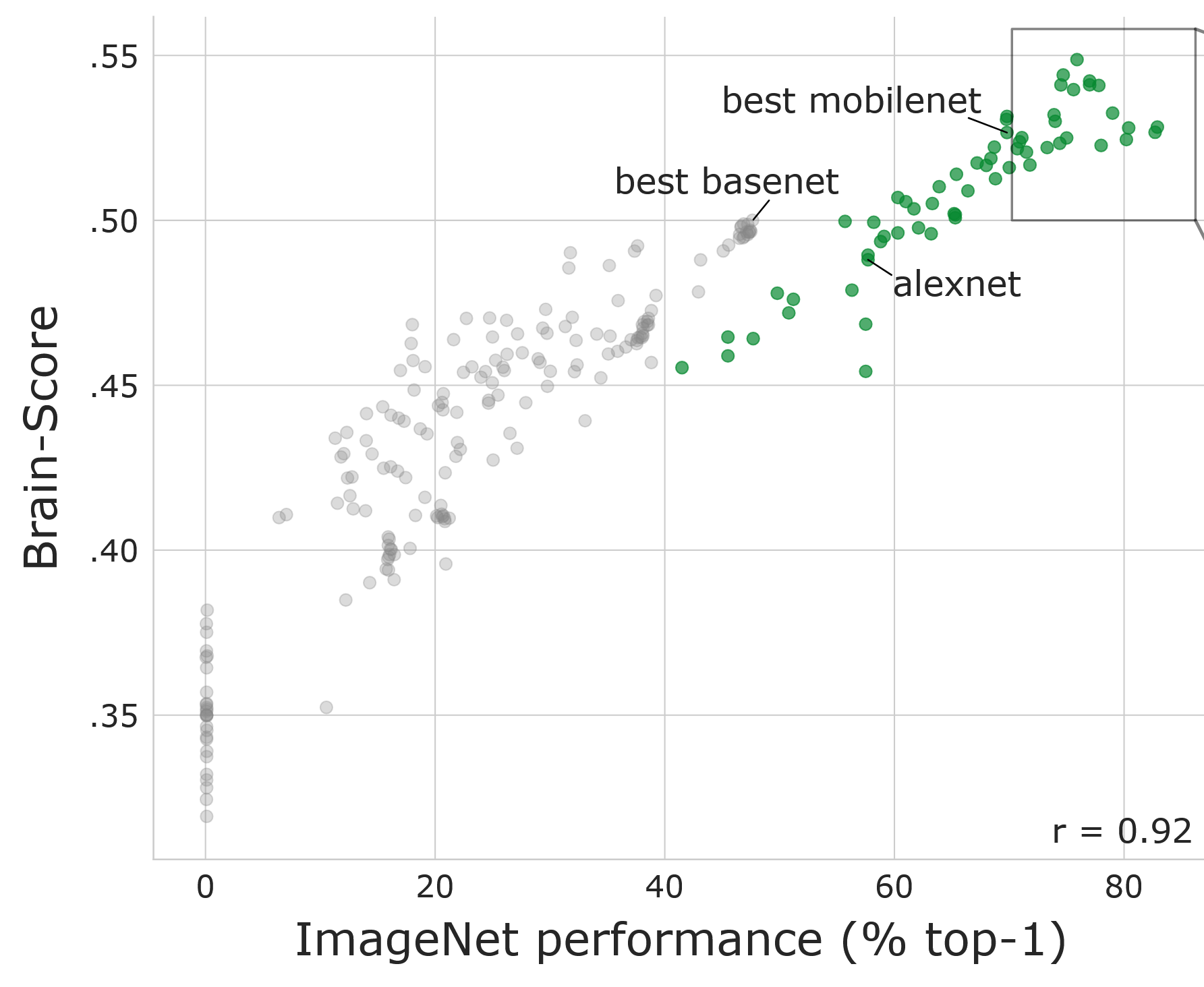
Schrimpf et al. (2018): Brain-score: Which artificial neural network for object recognition is most brain-like?
- Not every model maps onto the neural hierarchy
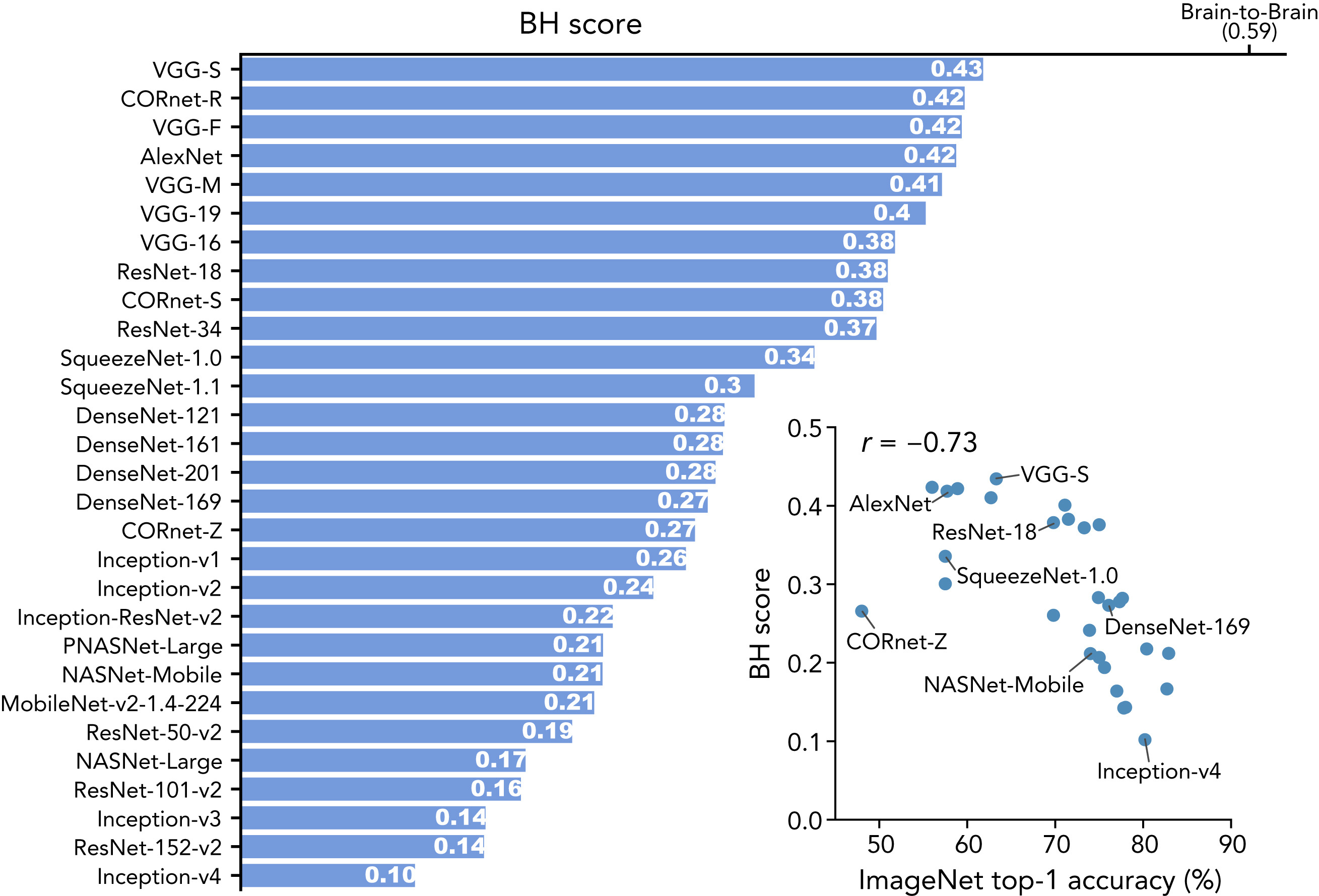
Nonaka et al. (2021): Brain hierarchy score: Which deep neural networks are hierarchically brain-like?
Comparing Humand and Model Behavior
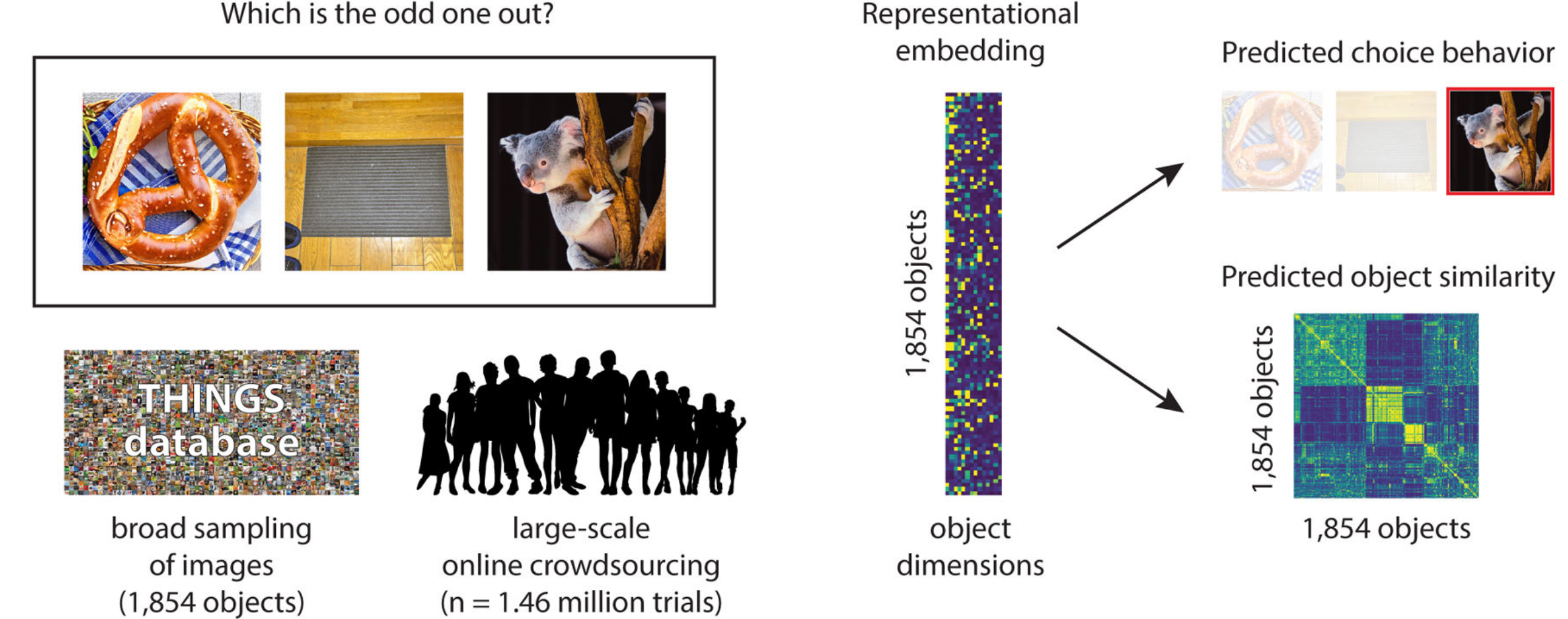

Different Dimensions of Interest
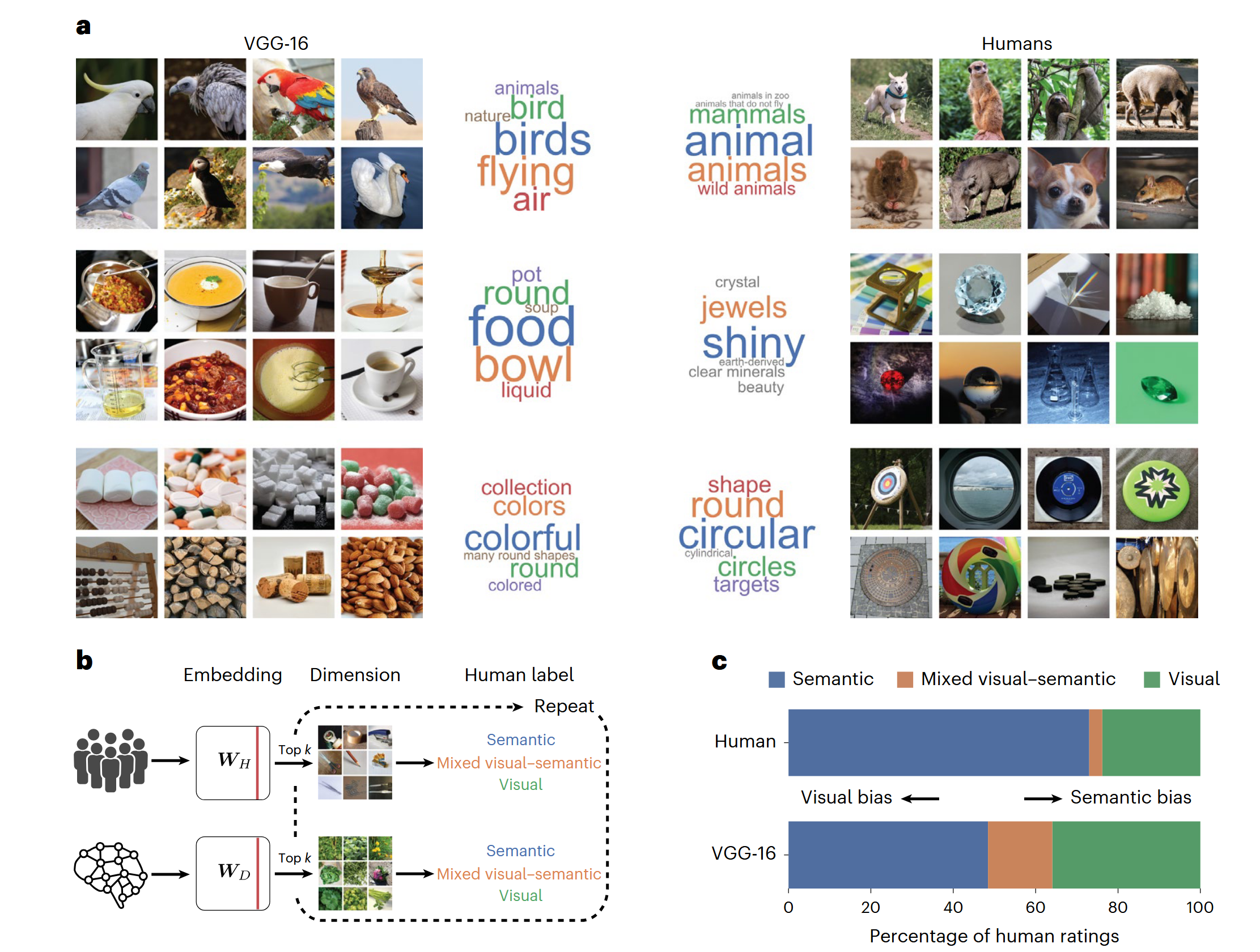
Fundamental Differences between Artifical and Biological Intelligence
Emodied Cognition
- AI is purely computational/statistical inference but human cognition is physically embodied
- Human cognition can extend beyond the brain into the body and environment
- Example: the gaze heuristic
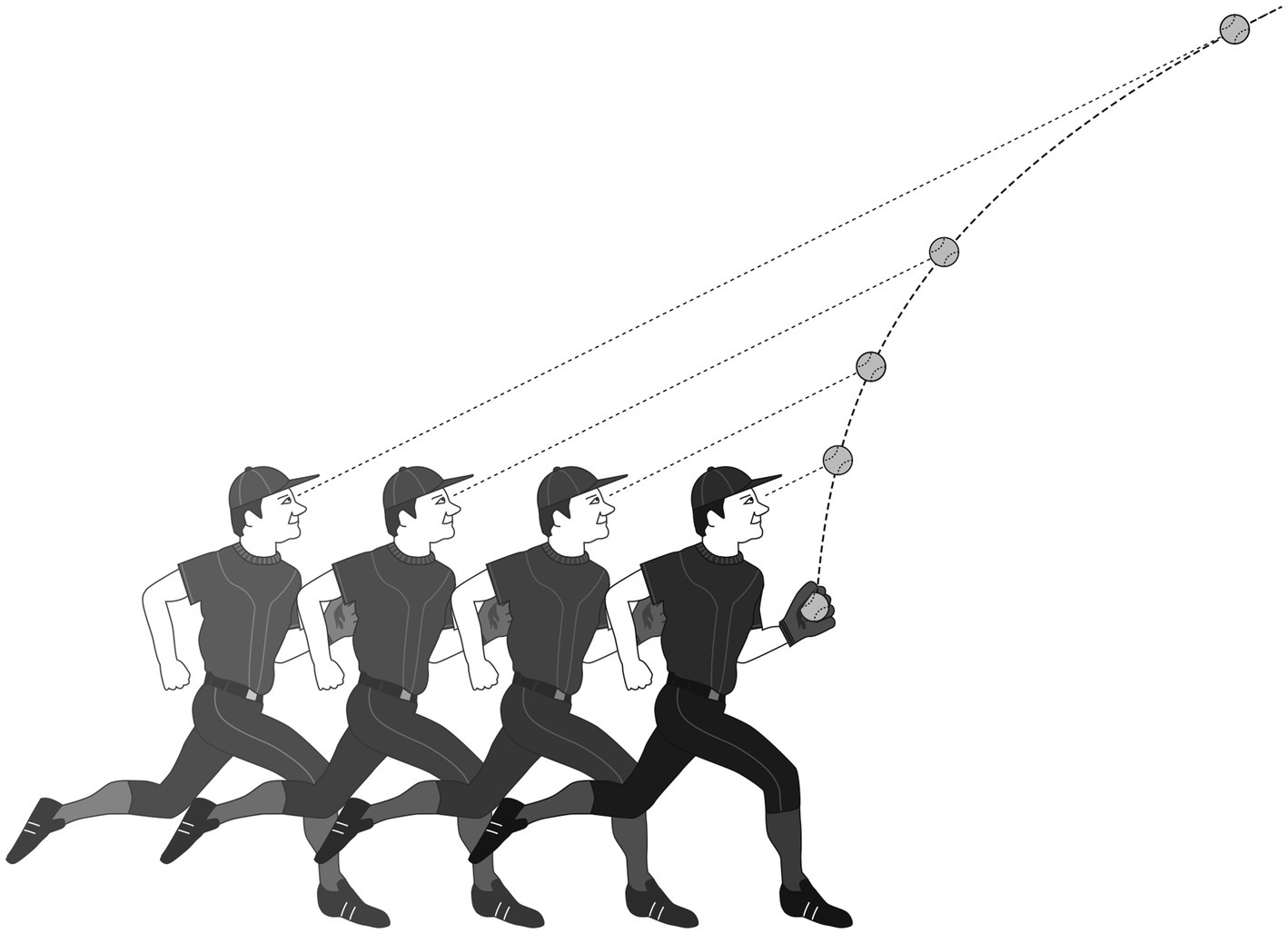
- Because human cognition is embodied, complicated inference problems can be solved by simple heuristics
Are AI “Agents” Real Agents?
Biological Agents
- Are autopoietic (i.e. self-manufacturing)
- Are internally motivated to self-preserve and act autonomously
- Live in a large world of ill-defined problems and have to decide what is relevant
Artificial Agents
- Are programmed by an external agent
- Are externally motivated and triggered by an external agent
- Live in a small world of well-defined problems and operate within predefined formalized ontology
See Jaeger et al. (2024): Naturalizing relevance realization: why agency and cognition are fundamentally not computational
Thank
you
Image Credits: razum /Shutterstock
References
Chollet, François. 2019. “On the Measure of Intelligence.” arXiv Preprint arXiv:1911.01547.
Gigerenzer, Gerd. 2021. “Embodied Heuristics.” Frontiers in Psychology 12: 711289.
Hebart, Martin N, Charles Y Zheng, Francisco Pereira, and Chris I Baker. 2020. “Revealing the Multidimensional Mental Representations of Natural Objects Underlying Human Similarity Judgements.” Nature Human Behaviour 4 (11): 1173–85.
Hebb, DO. 1949. “The Organization of Behavior. A Neuropsychological Theory.”
Jaeger, Johannes, Anna Riedl, Alex Djedovic, John Vervaeke, and Denis Walsh. 2024. “Naturalizing Relevance Realization: Why Agency and Cognition Are Fundamentally Not Computational.” Frontiers in Psychology 15: 1362658.
Mahner, Florian P, Lukas Muttenthaler, Umut Güçlü, and Martin N Hebart. 2025. “Dimensions Underlying the Representational Alignment of Deep Neural Networks with Humans.” Nature Machine Intelligence 7 (6): 848–59.
McCulloch, Warren S, and Walter Pitts. 1943. “A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity.” The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 5 (4): 115–33.
Nonaka, Soma, Kei Majima, Shuntaro C Aoki, and Yukiyasu Kamitani. 2021. “Brain Hierarchy Score: Which Deep Neural Networks Are Hierarchically Brain-Like?” IScience 24 (9).
Raugel, Joséphine, Marc Szafraniec, Huy V Vo, Camille Couprie, Patrick Labatut, Piotr Bojanowski, Valentin Wyart, and Jean-Rémi King. 2025. “Disentangling the Factors of Convergence Between Brains and Computer Vision Models.” arXiv Preprint arXiv:2508.18226.
Schrimpf, Martin, Jonas Kubilius, Ha Hong, Najib J Majaj, Rishi Rajalingham, Elias B Issa, Kohitij Kar, et al. 2018. “Brain-Score: Which Artificial Neural Network for Object Recognition Is Most Brain-Like?” BioRxiv, 407007.